Bronchospasm Emergency – What You Need to Know Fast
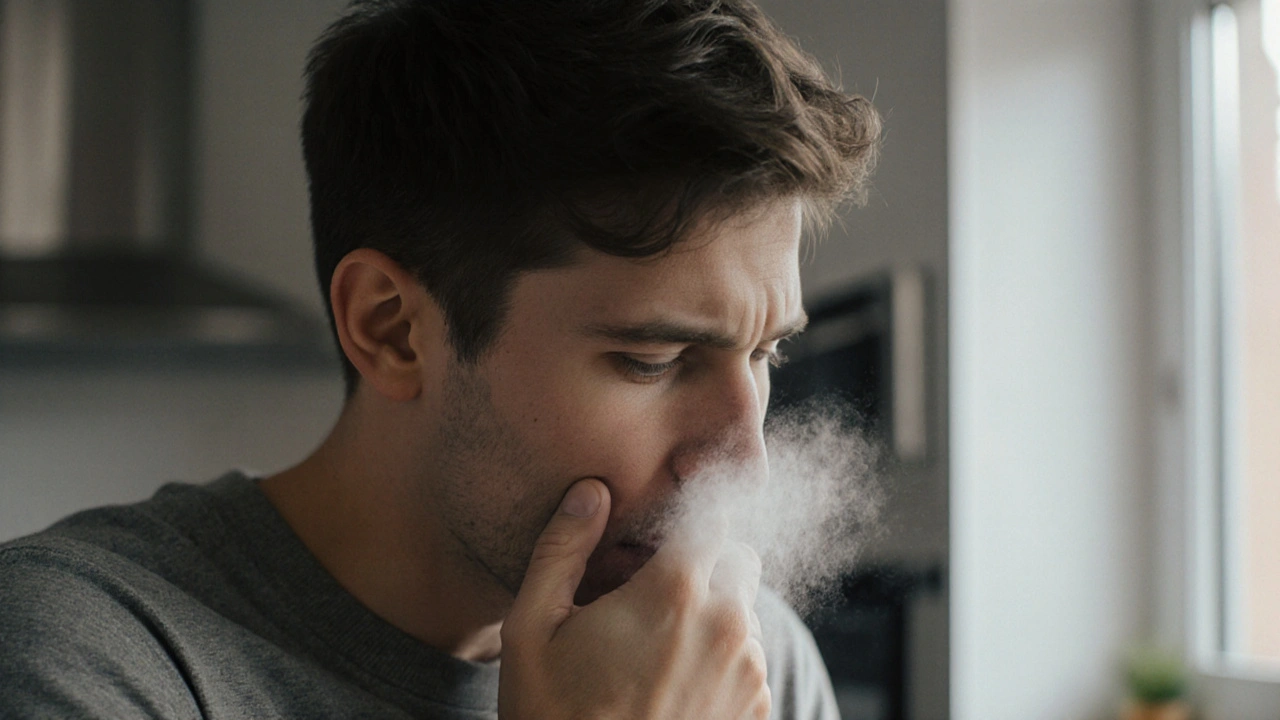
When facing a bronchospasm emergency, every second counts. Bronchospasm emergency, a sudden tightening of the airway muscles that blocks airflow and can cause severe breathing difficulty. Also known as acute bronchoconstriction, it often signals an underlying respiratory crisis. Understanding how this event ties to asthma, inhaler technology, and emergency medication helps you act before panic takes over.
One of the most common triggers is asthma attack, a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways that can flare into a bronchospasm. When the airway smooth muscle contracts, oxygen delivery drops, and the person may experience wheezing, chest tightness, and a feeling of suffocation. The link between asthma and bronchospasm is direct: asthma encompasses episodes of bronchoconstriction that can become emergencies if not treated promptly. Recognizing the warning signs—rapid breathing, inability to speak full sentences, and a bluish tinge around the lips—sets the stage for immediate intervention.
Key Steps to Manage a Bronchospasm Emergency
The first line of defense is a beta‑agonist inhaler, a handheld device that delivers medication to relax airway muscles quickly. These inhalers, such as albuterol or salbutamol, work by binding to beta‑2 receptors, causing the smooth muscle to relax and opening the airway within minutes. The semantic triple here is: bronchospasm emergency requires rapid bronchodilator administration. If the patient has a prescribed inhaler, encourage them to take two to four puffs, wait a minute, and repeat if necessary. For those without an inhaler, emergency services should be called without delay; epinephrine administered by a professional can also reverse severe bronchospasm.
Beyond inhalers, other related entities come into play. Epinephrine auto‑injector, a life‑saving injection used in extreme cases to widen airways and support blood pressure is often stocked in schools and workplaces for anaphylactic reactions, but it also serves as a backup for stubborn bronchospasm when standard inhalers fail. The relationship is clear: epinephrine influences bronchospasm emergency outcomes by providing a rapid, systemic bronchodilatory effect. Knowing when to switch from a local inhaler to an epinephrine shot can be the difference between a quick recovery and a critical situation.
Another useful tool is a peak flow meter, a portable device that measures how fast you can exhale, helping track airway narrowing. While not a treatment, it offers real‑time data that can alert patients to an impending bronchospasm before symptoms become severe. The semantic link: monitoring peak flow supports early detection of bronchospasm emergency risk. Regular use of a peak flow meter can guide medication adjustments and prevent emergencies altogether.
When a bronchospasm escalates despite quick inhaler use, supplemental oxygen should be administered if available. Oxygen therapy raises blood oxygen levels, buying time for advanced care. In a hospital setting, clinicians may add systemic steroids, which reduce airway inflammation over hours, and anticholinergic agents like ipratropium bromide for added bronchodilation. These therapies demonstrate another triple: bronchospasm emergency management often combines bronchodilators, steroids, and oxygen to restore breathing. Each component tackles a different aspect of the airway crisis—muscle constriction, swelling, and oxygen deficiency.
Finally, education and prevention cannot be ignored. Patients with known asthma or COPD should have an asthma action plan that outlines trigger avoidance, medication schedules, and emergency steps. Regular follow‑ups with a healthcare provider ensure inhaler technique is correct and that prescriptions are current. By staying ahead of triggers—like pollen, cold air, or exercise—the likelihood of a sudden bronchospasm drops dramatically. This proactive approach ties everything together: understanding causes, having the right tools, and acting swiftly creates a safety net against bronchospasm emergencies.
Below you’ll find a curated list of articles that dive deeper into each of these topics—from choosing the right inhaler to handling severe attacks in the field. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or health professional, the resources ahead will give you practical tips and trusted advice to handle a bronchospasm emergency with confidence.
How to Prepare for a Bronchospasm Emergency: Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to recognize, treat, and prevent bronchospasm emergencies with step‑by‑step action plans, essential supplies, inhaler technique tips, and when to call ambulance.
View More