Medication Interactions: What You Need to Know Before Taking Pills Together
When you take more than one medication, you’re not just adding effects—you’re creating a medication interaction, a biological or chemical reaction between two or more drugs that changes how they work in your body. Also known as drug interaction, it can make a pill useless, dangerously strong, or even toxic. This isn’t rare. Nearly half of adults take at least one prescription drug, and many add over-the-counter pills, vitamins, or herbal supplements. That’s a recipe for unintended consequences if you don’t know what’s happening inside your body.
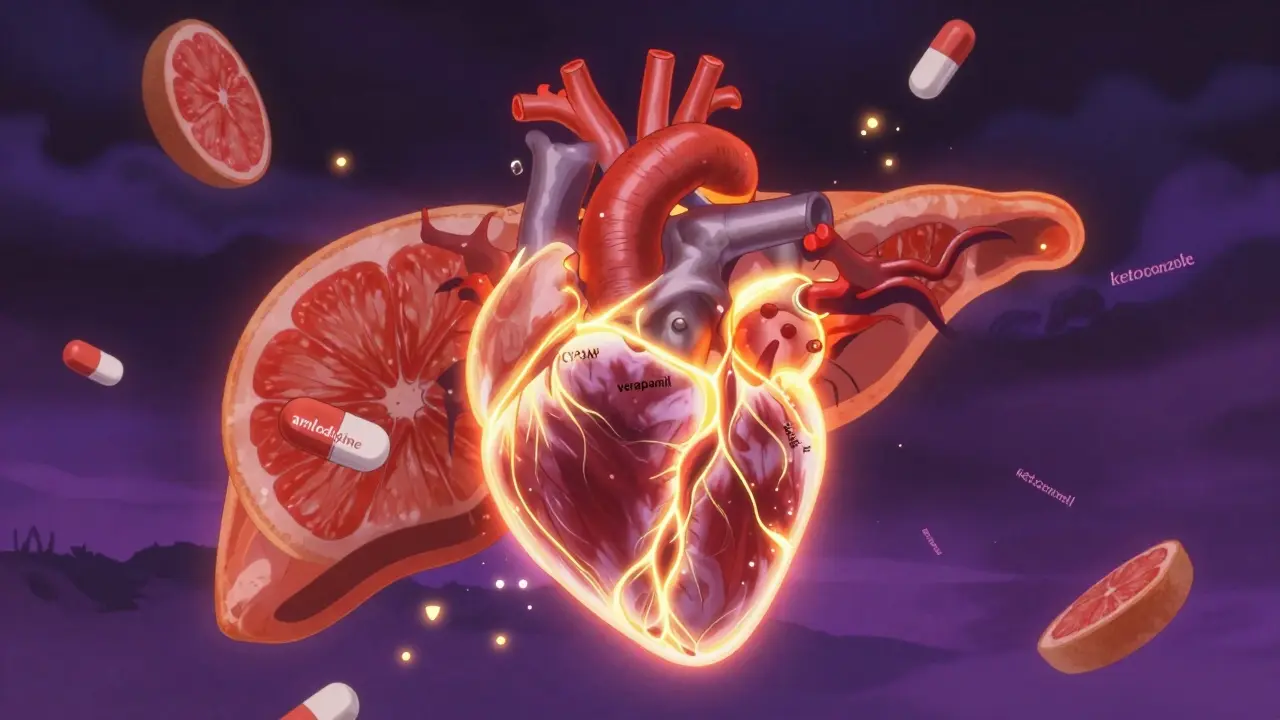
One of the most common polypharmacy, the use of multiple medications by a single patient, often for chronic conditions problems is when blood pressure drugs like olmesartan or amlodipine mix with NSAID gels or even common painkillers. The result? Your blood pressure might not drop, or your kidneys could get stressed. Or take combination therapy, a treatment approach using lower doses of multiple drugs to reduce side effects while maintaining effectiveness. It sounds smart—until you realize one of those drugs blocks the other from working. That’s why knowing how levamisole affects bird metabolism or how nitrofurantoin triggers hemolytic anemia in people with G6PD deficiency matters. These aren’t edge cases—they’re real-world examples of how the same principle applies across humans and animals.
It’s not just about prescriptions. That daily vitamin? That ginger tea for nausea? That OTC sleep aid you grab when you can’t shut off your brain? All of them can interact. Ketoconazole can mess with liver enzymes that break down other drugs. Trazodone can make sedatives too strong. Even expired pills might not be harmless—potency drops, and chemical breakdowns can create new compounds your body doesn’t expect. And if you’re managing depression, you’re more likely to forget doses or take them wrong, which changes how interactions play out. It’s not just what you take—it’s when, how much, and why.
You don’t need to be a pharmacist to stay safe. But you do need to ask the right questions. What else are you taking? Are you mixing old and new meds? Did your doctor check for interactions when they added that new pill? The posts below cover exactly this: how to spot dangerous combinations, what to do if you’re traveling and lose your meds, how certain drugs like tenofovir or chloramphenicol carry hidden risks, and how even something as simple as alcohol can change how your heart responds to treatment. This isn’t theory. These are real stories, real science, and real fixes—put together so you don’t have to guess what’s safe.
Calcium Channel Blockers: How Metabolic Interactions Affect Drug Clearance and Safety
Calcium channel blockers are widely used for high blood pressure and heart conditions, but their safety depends heavily on how they interact with other drugs and your liver's ability to clear them. Learn which ones are safest and how to avoid dangerous interactions.
View MoreHow to Use a Drug Interaction Checker Tool Effectively
Learn how to use a drug interaction checker tool effectively to avoid dangerous medication combinations. Discover which tools are most accurate, how to interpret alerts, and why you should always confirm results with a pharmacist.
View More