Calcium Channel Blockers: How They Work, Common Types, and What You Need to Know
When your heart and blood vessels need to relax, calcium channel blockers, a class of medications that prevent calcium from entering heart and blood vessel cells. Also known as calcium antagonists, they’re one of the most common treatments for high blood pressure and angina. These drugs don’t just lower blood pressure—they help your heart work less hard by slowing down the signals that make blood vessels tighten. That’s why they’re often the first or second choice for people with hypertension, especially older adults or those with certain heart conditions.
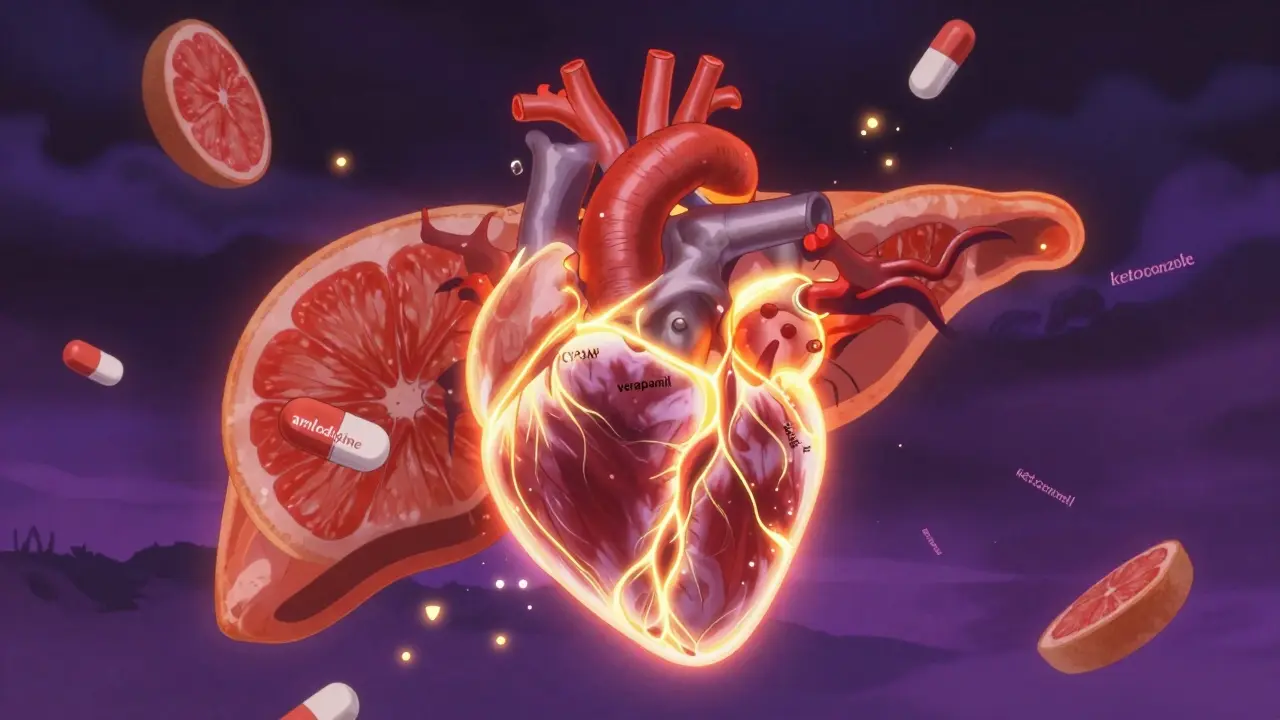
Not all calcium channel blockers are the same. Some, like amlodipine, a long-acting dihydropyridine used daily to control blood pressure, work mostly on blood vessels. Others, like verapamil, a non-dihydropyridine that also slows heart rate, affect both the heart and vessels. Then there’s nifedipine, a fast-acting option sometimes used for sudden spikes in blood pressure or Raynaud’s phenomenon. Each has its own rhythm, timing, and side effect profile. You might take one daily, or your doctor might combine it with other meds—like an ARB or diuretic—to get better control with lower doses, reducing the chance of dizziness or swelling in your ankles.
People often wonder if these drugs are safe long-term. The answer is usually yes, especially when monitored. But they’re not for everyone. If you have certain heart rhythm problems, severe low blood pressure, or liver disease, your doctor will pick another option. And while they’re not addictive, skipping doses or stopping cold turkey can make your blood pressure spike dangerously. That’s why it’s important to understand how they fit into your daily routine—whether you’re taking them with food, avoiding grapefruit juice, or managing side effects like headaches or fatigue.
What you’ll find below are real-world guides on how calcium channel blockers interact with other meds, how they’re used in combo therapy, and how to spot when they’re working—or when something’s off. You’ll see comparisons with alternatives, stories about managing side effects, and practical tips from people who’ve been on them for years. No fluff. Just clear, usable info that helps you take control without guesswork.
Calcium Channel Blockers: How Metabolic Interactions Affect Drug Clearance and Safety
Calcium channel blockers are widely used for high blood pressure and heart conditions, but their safety depends heavily on how they interact with other drugs and your liver's ability to clear them. Learn which ones are safest and how to avoid dangerous interactions.
View MoreDiltiazem HCL vs Alternatives: What Works Best for High Blood Pressure and Angina
Diltiazem HCL is effective for high blood pressure and angina, but alternatives like Amlodipine, Lisinopril, and Metoprolol may offer better tolerance or results. Learn how they compare in effectiveness, side effects, and cost.
View More